Embark on an enriching journey into the realm of oxidation numbers with our meticulously crafted Assigning Oxidation Numbers Practice Worksheet. This comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and skills to master this fundamental concept in chemistry.
Through a series of engaging exercises and step-by-step guidance, you will delve into the significance of oxidation numbers in chemical reactions, unravel the rules and exceptions governing their assignment, and uncover the practical applications that make them indispensable in the field of chemistry.
Assigning Oxidation Numbers Practice Worksheet

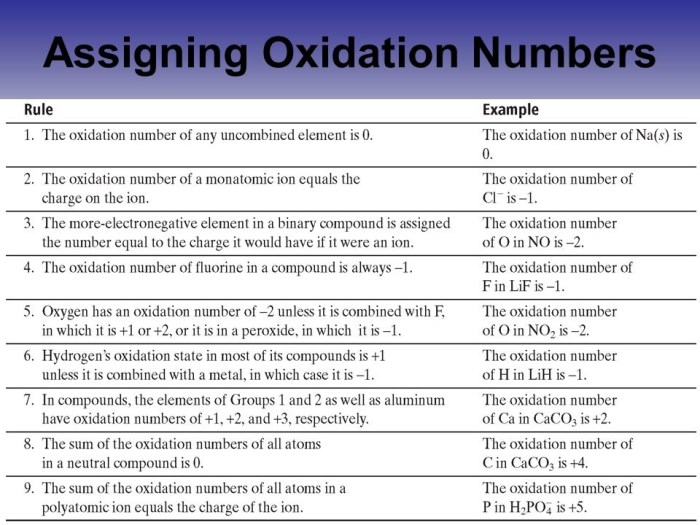
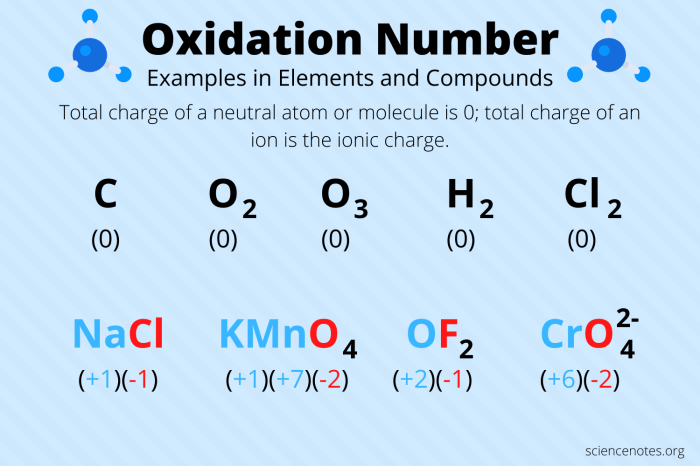
Oxidation numbers are a crucial concept in chemistry that represent the oxidation state of individual atoms within a compound or molecule. Assigning oxidation numbers allows us to understand the distribution of electrons and the changes that occur during chemical reactions.
This practice worksheet provides exercises to help students master the skill of assigning oxidation numbers to various chemical compounds. By working through these exercises, students will gain a deeper understanding of this fundamental chemical concept.
Practice Worksheet
- Assign oxidation numbers to all atoms in the following compounds:
- NaCl
- H2O
- CO 2
- NH 3
- Fe 2O 3
- Identify the element with the highest oxidation number in each of the following compounds:
- KMnO 4
- H 2SO 4
- Cr 2O 72-
- NO 3–
- MnO 2
- Assign oxidation numbers to the underlined atoms in the following compounds:
- CH 4
- O2
- NH 4+
- SO 42-
- PO 43-
Step-by-Step Guide to Assigning Oxidation Numbers
Follow these steps to assign oxidation numbers to atoms in a chemical compound:
- Assign the most electronegative element a negative oxidation number equal to the number of electrons it needs to gain to achieve a noble gas configuration.
- Assign the least electronegative element a positive oxidation number equal to the number of electrons it needs to lose to achieve a noble gas configuration.
- The sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound must be zero.
- The sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a polyatomic ion must be equal to the charge of the ion.
Common Errors, Assigning oxidation numbers practice worksheet
- Assigning an incorrect oxidation number to the most electronegative element.
- Assigning an incorrect oxidation number to the least electronegative element.
- Forgetting to account for the charge of polyatomic ions.
- Confusing oxidation number with electronegativity.
Applications
Assigning oxidation numbers has practical applications in chemistry, including:
- Balancing chemical equations
- Understanding redox reactions
- Predicting the reactivity of chemical species
FAQ Explained: Assigning Oxidation Numbers Practice Worksheet
What is the purpose of assigning oxidation numbers?
Assigning oxidation numbers allows us to determine the oxidation state of each atom in a compound or ion, providing insights into the electron transfer processes occurring during chemical reactions.
How do I determine the oxidation number of an atom?
Follow the step-by-step guide provided in the practice worksheet, which Artikels the rules and exceptions for assigning oxidation numbers based on the atom’s position, electronegativity, and bonding.
What are common errors to avoid when assigning oxidation numbers?
The practice worksheet highlights common errors, such as assigning an incorrect oxidation number to hydrogen or oxygen, and provides examples to illustrate why these assignments are incorrect.