Financial and managerial accounting information for decisions 9th edition – Financial and Managerial Accounting Information for Decisions, 9th Edition, delves into the transformative power of accounting data in empowering decision-makers. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of financial statement analysis, cost accounting, budgeting, performance measurement, and ethical considerations, equipping readers with the knowledge to navigate complex business landscapes and make informed choices.
Throughout this captivating journey, we will explore the diverse applications of accounting information, from identifying financial strengths and weaknesses to optimizing operations and mitigating risks. Real-world case studies and practical examples bring the concepts to life, showcasing the tangible impact of accounting insights on organizational success.
Introduction to Financial and Managerial Accounting Information

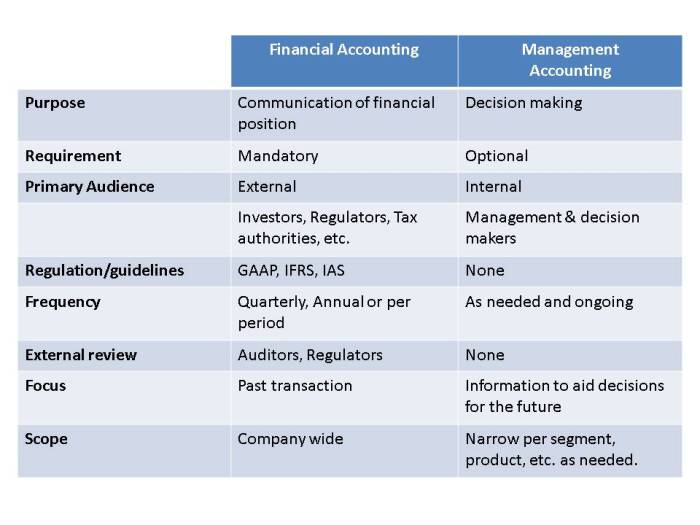
Financial and managerial accounting information is crucial for decision-making in organizations. It provides insights into the financial health, performance, and operations of a business. Financial accounting focuses on external reporting, while managerial accounting supports internal decision-making.
Types of financial and managerial accounting information include financial statements, budgets, forecasts, cost analyses, and performance metrics. These can be used to:
- Assess financial performance and risk
- Plan for the future and mitigate risks
- Optimize operations and improve profitability
- Measure and evaluate performance
Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statements provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial position and performance. They include:
- Balance sheet: Shows assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time
- Income statement: Reports revenues, expenses, and net income over a period of time
- Cash flow statement: Summarizes cash inflows and outflows
Key financial ratios and metrics used in analysis include:
- Liquidity ratios: Measure a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations
- Solvency ratios: Assess a company’s long-term financial health
- Profitability ratios: Evaluate a company’s profitability and efficiency
Cost Accounting and Analysis: Financial And Managerial Accounting Information For Decisions 9th Edition
Cost accounting provides information about the costs of products, services, or activities. Types of costing systems include:
- Job costing: Tracks costs for specific jobs or projects
- Process costing: Allocates costs to units produced in a continuous process
- Activity-based costing (ABC): Assigns costs to activities and then to products or services
Cost analysis techniques include:
- Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis: Examines the relationship between costs, volume, and profit
- Break-even analysis: Determines the point at which revenue equals total costs
Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting involves planning and allocating resources for future operations. Types of budgets include:
- Operating budget: Covers day-to-day operations
- Capital budget: Artikels investments in long-term assets
- Cash budget: Forecasts cash inflows and outflows
Forecasting involves predicting future financial performance. Techniques include:
- Time series analysis: Uses historical data to predict future trends
- Regression analysis: Estimates the relationship between variables to predict future values
Performance Measurement and Evaluation
Performance measurement and evaluation assess how well an organization is achieving its goals. Methods include:
- Key performance indicators (KPIs): Measure specific aspects of performance
- Balanced scorecard: Provides a comprehensive view of performance across multiple perspectives
- Return on investment (ROI): Evaluates the financial return on investments
Performance evaluation can identify areas for improvement and support decision-making.
Ethical Considerations in Financial and Managerial Accounting
Financial and managerial accounting professionals must adhere to ethical principles and standards. Potential ethical dilemmas include:
- Misrepresentation of financial information
- Conflicts of interest
- Breach of confidentiality
Ethical considerations can influence decision-making and promote transparency and accountability.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Case studies demonstrate the practical application of financial and managerial accounting information. They provide insights into:
- How organizations use accounting information to make informed decisions
- The challenges and opportunities associated with using accounting information
- Best practices and lessons learned from real-world examples
Case studies help bridge the gap between theory and practice.
FAQ Corner
What are the key benefits of using financial and managerial accounting information?
Enhanced decision-making, improved financial performance, optimized operations, and increased organizational effectiveness.
How can financial statement analysis help businesses identify trends and weaknesses?
By examining key financial ratios and metrics, businesses can uncover patterns, assess financial health, and pinpoint areas for improvement.
What is the role of cost accounting in optimizing operations?
Cost accounting provides insights into the costs associated with products or services, enabling businesses to identify inefficiencies, reduce expenses, and improve profitability.
How can budgeting and forecasting mitigate risks and plan for the future?
Budgets and forecasts allow businesses to anticipate financial needs, allocate resources effectively, and prepare for potential challenges.
What are the ethical considerations that financial and managerial accountants must adhere to?
Accountants are bound by ethical principles that emphasize accuracy, objectivity, confidentiality, and professional integrity.